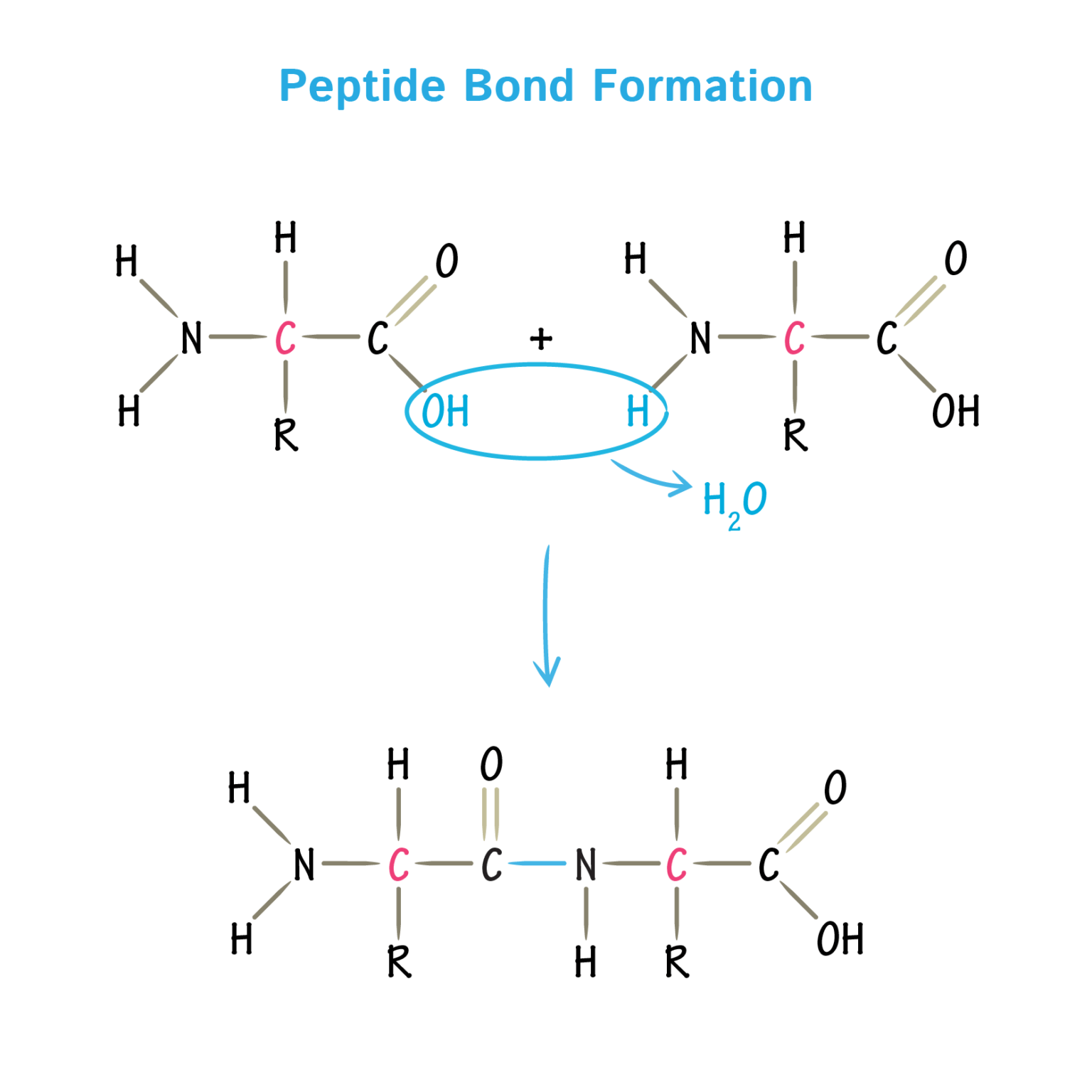
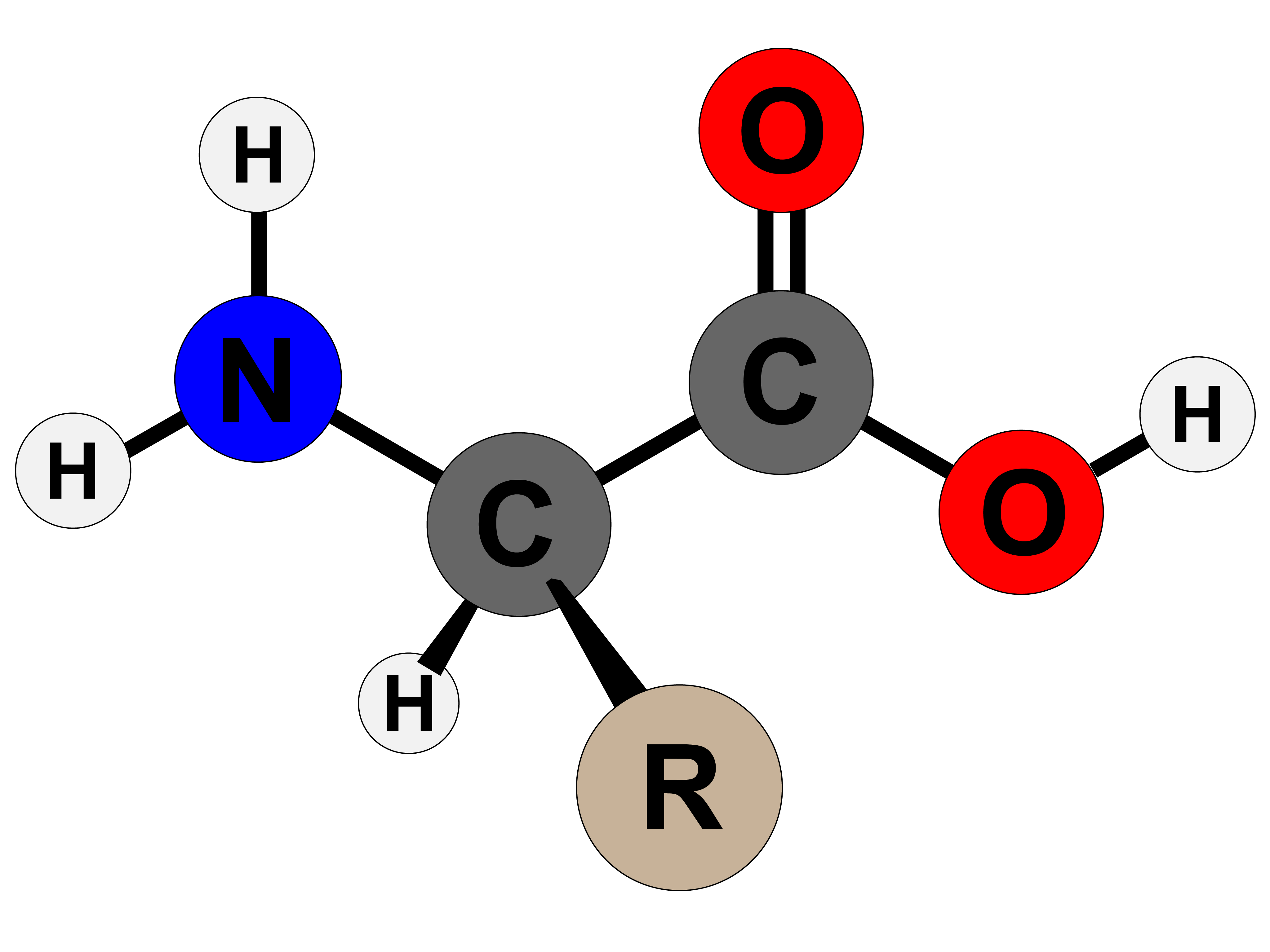
Drawing Of Amino Acid
Drawing Of Amino Acid - These small changes will have a huge impact on the structure and function of proteins. However, it is not uncommon for other elements to be found in the side chain of an amino acid. Web all amino acids have the same basic structure, which is shown in figure 2.1. Amino and carboxyl groups, side chains, and zwitterions. When drawing an individual amino acid, the amine will be positively charged and the carbonyl will be negatively charged. Alanine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, and valine. Account for some of the typical properties of amino acids (e.g., high melting points, solubility in water) in terms of zwitterion formation. Account for some of the typical properties of amino acids (e.g., high melting points, solubility in water) in terms of zwitterion formation. Web classify an amino acid as being acidic, basic or neutral, given its kekulé, condensed or shorthand structure. Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. From the illustration, it can be noted that the key elements that make up amino acids are hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. Web every amino acid that we’re covering in this tutorial starts out with the same basic structure (picture 1). When drawing an individual amino acid, the amine will be positively charged and the carbonyl will be negatively charged. Web from a structural perspective, amino acids are typically composed of a carbon atom, a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group along with an amino group and a variable group. Web chemistry of life >. Web classify an amino acid as being acidic, basic or neutral, given its kekulé, condensed or shorthand structure. Alanine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, and valine. Properties, structure, and function of biological macromolecules. Web the major building blocks of proteins are called alpha (α) amino acids. Account for some of the typical properties of amino acids (e.g., high melting points, solubility in water) in terms of zwitterion formation. Properties, structure, and function of biological macromolecules. Amino acids and the central dogma of molecular biology. Web from a structural perspective, amino acids are typically composed of a carbon atom, a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group along with an amino group and a variable group. Web every amino acid that we’re covering in this tutorial starts out with the same. Web classify an amino acid as being acidic, basic or neutral, given its kekulé, condensed or shorthand structure. As their name implies they contain a carboxylic acid functional group and an amine functional group. However, it is not uncommon for other elements to be found in the side chain of an amino acid. Draw fisher projections and assign d/l or. Draw fisher projections and assign d/l or r/s stereodescriptors to proteinogenic amino acids. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom. A downloadable study sheet of this information is available here. Web. To connect amino acids together, a peptide bond (also called an amide bond). Based on the variable group, amino acids can be classified into four categories: Draw the zwitterion form of a given amino acid. Web the general structure of an amino acid is illustrated below. A downloadable study sheet of this information is available here. Draw fisher projections and assign d/l or r/s stereodescriptors to proteinogenic amino acids. Web all amino acids have the same basic structure, shown in figure 2.1. As their name implies they contain a carboxylic acid functional group and an amine functional group. Web classify an amino acid as being acidic, basic or neutral, given its kekulé, condensed or shorthand structure.. Web karen steward, phd. Web all amino acids have the same basic structure, which is shown in figure 2.1. Web they contain an amino group, carboxylic acid group, alpha carbon, and side chain. Web from a structural perspective, amino acids are typically composed of a carbon atom, a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group along with an amino group and a. Draw the zwitterion form of a given amino acid. Web classify an amino acid as being acidic, basic or neutral, given its kekulé, condensed or shorthand structure. Based on the variable group, amino acids can be classified into four categories: Draw fisher projections and assign d/l or r/s stereodescriptors to proteinogenic amino acids. Draw the zwitterion form of a given. On one end there is an amine and on the other end is a carbonyl. When drawing an individual amino acid, the amine will be positively charged and the carbonyl will be negatively charged. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino. Web the general structure of an amino acid is illustrated below. From the illustration, it can be noted that the key elements that make up amino acids are hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. Draw the zwitterion form of a given amino acid. Nonpolar, polar, negatively charged, and positively charged. Alanine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, and valine. Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. Draw the zwitterion form of a given amino acid. Account for some of the typical properties of amino acids (e.g., high melting points, solubility in water) in terms of zwitterion formation. Amino acids are the building blocks that form polypeptides and ultimately proteins. Web all amino acids have the same basic. These small changes will have a huge impact on the structure and function of proteins. Draw the zwitterion form of a given amino acid. Web the major building blocks of proteins are called alpha (α) amino acids. Created by tracy kim kovach. Properties, structure, and function of biological macromolecules. Web all amino acids have the same basic structure, which is shown in figure 2.1. Nonpolar, polar, negatively charged, and positively charged. On one end there is an amine and on the other end is a carbonyl. Learn how to draw alpha amino acids and primary structure of proteins in this video lesson! Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Web how to draw amino acids and peptide bonds to make a protein. Draw the zwitterion form of a given amino acid. Web classify an amino acid as being acidic, basic or neutral, given its kekulé, condensed or shorthand structure. Amino and carboxyl groups, side chains, and zwitterions. Web they contain an amino group, carboxylic acid group, alpha carbon, and side chain. Web memorize the amino acid names and structures as quickly as possible, but take the time to understand the physical processes that affect amino acids.Amino Acid Flat Line Icon. Vector Outline Illustration of Structural
Amino Acids. biochemanics
Amino Acids — Overview & Structure Expii
Amino acids physical, chemical properties and peptide bond
Amino Acid Labeled Diagram Vector Illustration Drawing Biochemistry
Amino acids structure vector illustration infographic Amino acids
Basic Amino Acid Structure
Biochemistry Glossary Amino Acids Charged Draw It to Know It
How To Draw Amino Acids Structures Learn Mnemonics YouTube
Amino_Acid_Structure
Web Chemistry Of Life >.
Web Karen Steward, Phd.
The Alpha Designation Is Used To Indicate That These Two Functional Groups Are Separated From One Another By One Carbon Group.
Draw The Zwitterion Form Of A Given Amino Acid.
Related Post: