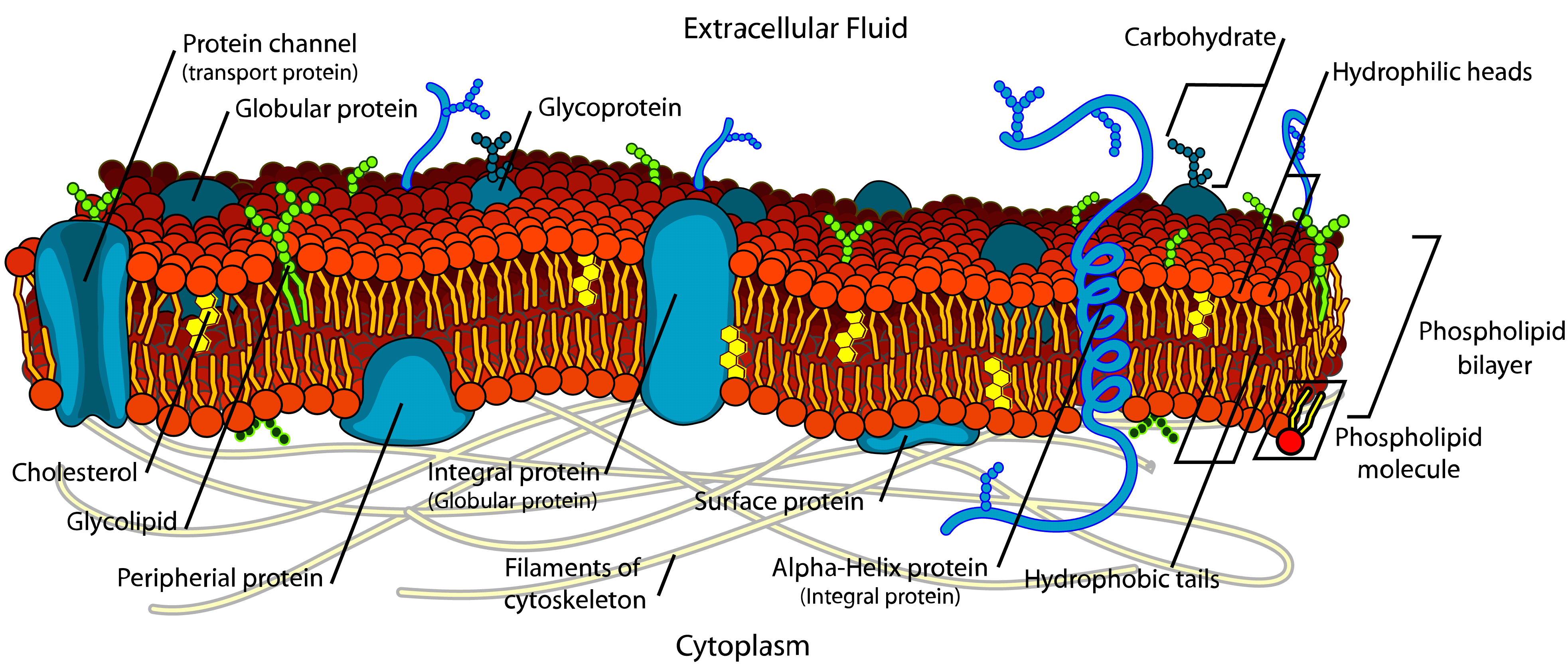
Cellplasma Membrane Drawing
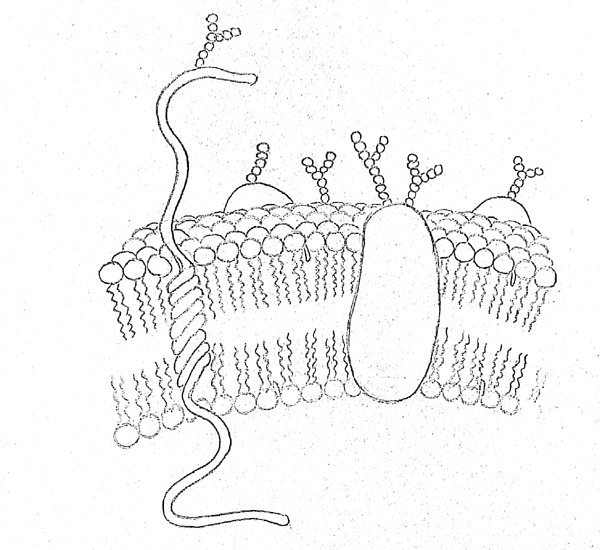
Cellplasma Membrane Drawing - Structure and function of the cell membrane. It separates the cytoplasm (the contents of the cell) from the external environment. Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. This theory is called the fluid mosaic model. Web a plasma membrane is a layer around a cell that prevents the cytoplasm from getting all mixed up with the outside environment. Web as the outer layer of your skin separates your body from its environment, the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) separates the inner contents of a cell from its exterior environment. In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell. Structure and composition of the cell (plasma) membrane. Web what is a cell (plasma) membrane and what it does in a cell: Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have plasma membranes, but they vary among different organisms. It is also simply called the cell membrane. Web a cell’s plasma membrane defines the cell, outlines its borders, and determines the nature of its interaction with its environment. Web the plasma membrane of a cell is a network of lipids and proteins that forms the boundary between a cell’s contents and the outside of the cell. It is the membrane found in all cells, that separate the inner part of the cell from the exterior. The membrane is also covered in places with cholesterol molecules and. A 3d diagram of the cell membrane. The cell membrane is semipermeable (or selectively permeable). The plasma membrane not only defines the borders of the cell, but also allows the cell to interact with its environment in a controlled way. Functions and diagram of cell (plasma) membranes. Its facts, analogy, composition, location, & functions described using examples & labeled picture. Web what is a cell (plasma) membrane and what it does in a cell: Plasma membrane (cell membrane) is made of two phospholipid layers, or a type of lipid with hydrophilic. Web the plasma membrane is a protective barrier that surrounds cells. Web as the outer layer of your skin separates your body from its environment, the cell membrane (also. The cell membrane is semipermeable (or selectively permeable). Cells exclude some substances, take in others, and excrete still others, all in controlled quantities. This theory is called the fluid mosaic model. It is also simply called the cell membrane. Plasma membrane (cell membrane) is made of two phospholipid layers, or a type of lipid with hydrophilic. The main function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surrounding environment. This study has conducted uniaxial. The plasma membrane not only defines the borders of the cell, but also allows the cell to interact with its environment in a controlled way. A 3d diagram of the cell membrane. It is the membrane found in all. This theory is called the fluid mosaic model. It is made of a phospholipid bilayer, along with other various lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. It is the membrane found in all cells, that separate the inner part of the cell from the exterior. Cholesterol and various proteins are also embedded within the membrane giving the membrane a variety of functions described. Structure and composition of the cell (plasma) membrane. However, the proteome of prp in mares, particularly those susceptible to pbie, remains. Cholesterol and various proteins are also embedded within the membrane giving the membrane a variety of functions described below. Image modified from openstax biology. Its facts, analogy, composition, location, & functions described using examples & labeled picture. Structure and composition of the cell (plasma) membrane. It is the membrane found in all cells, that separate the inner part of the cell from the exterior. Web plasma membrane definition. Web the cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of two layers of phospholipids (a “bilayer”). It is made of a phospholipid bilayer, along with other various. Its facts, analogy, composition, location, & functions described using examples & labeled picture. Cells exclude some substances, take in others, and excrete still others, all in controlled quantities. Web plasma membrane is also referred to as the cell membrane. Web what are cellular membranes made of? In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the. Cells must be able to exclude, take in, and excrete various substances, all in specific amounts. Structure and function of the cell membrane. This theory, compared to earlier theories, best explains both microscopic observations and the function of the plasma membrane. Web reportedly, structural failures in membrane structures have occurred frequently, mostly originating from localized damage caused by intense loads. The cell membrane is semipermeable (or selectively permeable). Web the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space). With few exceptions, cellular membranes — including plasma membranes and internal membranes. Web a plasma membrane is a layer around a cell that prevents the cytoplasm from getting all mixed up with the outside environment. This study has conducted uniaxial. Web what are cellular membranes made of? Web what is a cell (plasma) membrane and what it does in a cell: Cells exclude some substances, take in others, and excrete still others,. Web like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. A cell wall is found to be attached to the plasma membrane to its exterior in plant and bacterial cells. Functions and diagram of cell (plasma) membranes. Web all cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. It is made of a phospholipid bilayer, along with other various lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. Web what are cellular membranes made of? Web the plasma membrane of a cell is a network of lipids and proteins that forms the boundary between a cell’s contents and the outside of the cell. Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. Cholesterol and various proteins are also embedded within the membrane giving the membrane a variety of functions described below. The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. Cells exclude some substances, take in others, and excrete still others, all in controlled quantities. Nicolson proposed a new model of the plasma membrane. However, the proteome of prp in mares, particularly those susceptible to pbie, remains. Each phospholipid is amphipathic, with two hydrophobic tails and a hydrophilic head. The cell membrane is semipermeable (or selectively permeable). Cells must be able to exclude, take in, and excrete various substances, all in specific amounts.Plasma Membrane In Plant Cell
The Plasma Membrane Our Virtual Classroom
Cell Organelles BIOLOGY JUNCTION
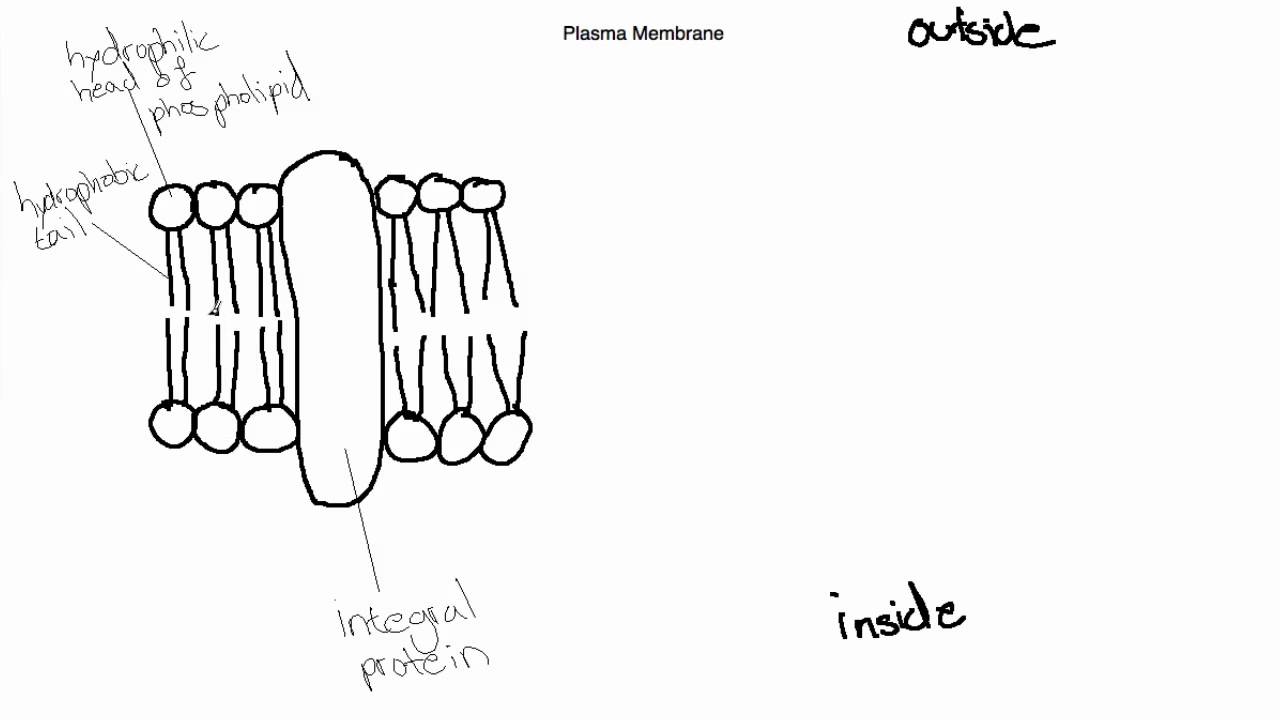
DRAW IT NEAT How to draw plasma membrane (Cell membrane)
Cell Membrane Function and Structure
Plasma Membrane Structure And Function Free Biology
Cell Membrane Introduction, Structure & Function
Cell Biology Glossary Membrane Structure Overview Draw It to Know It
Realistic human cell anatomy infographics with diagram showing plasma
IB Biology Topic 2.4.1 Draw and Label the Plasma Membrane YouTube
It Separates The Cytoplasm (The Contents Of The Cell) From The External Environment.
Web Reportedly, Structural Failures In Membrane Structures Have Occurred Frequently, Mostly Originating From Localized Damage Caused By Intense Loads On The Membrane Surface.
Because The Membrane Lets Some Things Through But Not.
Structure And Composition Of The Cell (Plasma) Membrane.
Related Post:

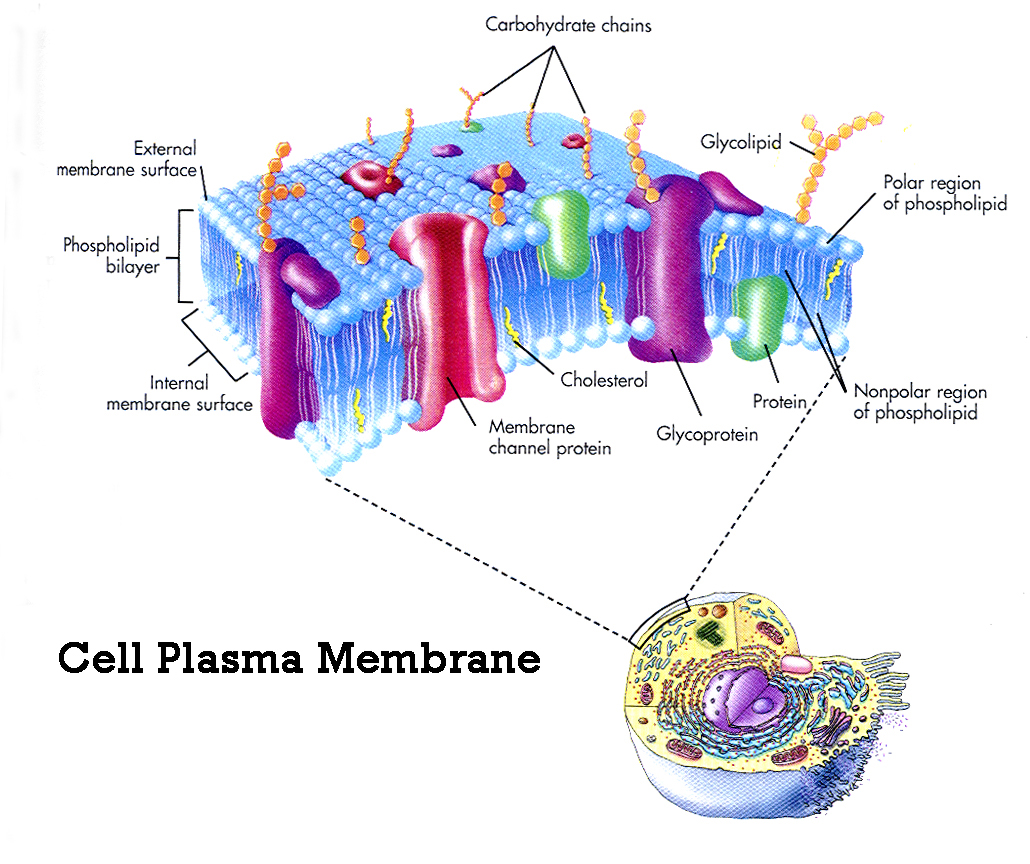
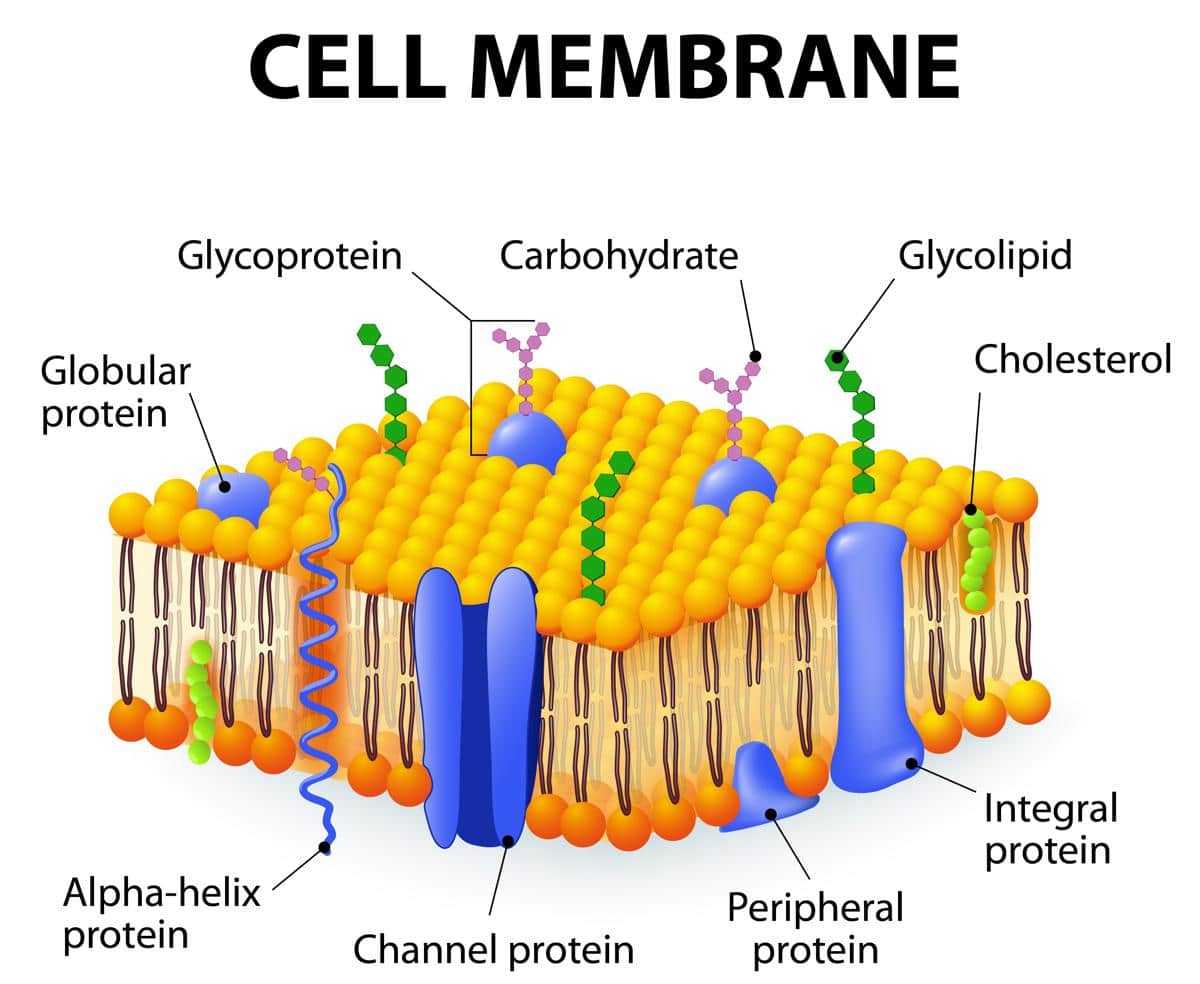
/plasma_membrane-58a617c53df78c345b5efb37.jpg)